AV1 Codec - Partition
In the AOM AV1 codec, partitioning refers to the division of a video image (frame) into smaller blocks in order to compress them more efficiently.
With the AV1 codec, the image is first divided into large blocks, for example, 128×128 pixel units. These blocks can be further subdivided depending on the image content – recursively and very flexibly.
AV1 supports various types of partitions: square, rectangular, asymmetric ("ab" shapes), as well as particularly stretched variants such as 1:4 or 4:1.
The goal of this division is to analyze complex or moving image areas as finely as possible, while compressing calm, uniform areas more coarsely. This allows for both efficient and high-quality encoding, while saving storage space and bandwidth.
Advertisement
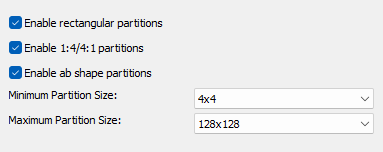
Enable rectangular partitions
Allows the codec to use rectangular blocks instead of just square blocks to divide the image. This increases the flexibility and efficiency of the coding.
Enable 1:4/4:1 partitions
Allows for particularly elongated block shapes, where a block is either four times taller than wide or four times wider than tall. This can be useful in scenes with highly directional structures.
Enable ab shape partitions
Allows special partitioning forms in which a block is divided asymmetrically into two parts of different sizes (“a” and “b”).
Minimum Partition Size
Specifies the smallest block size the codec can use when partitioning.
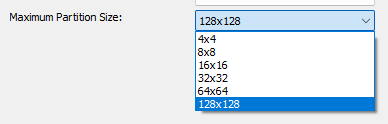
Maximum Partition Size
Specifies the largest block size the codec is allowed to use when partitioning.
Finer partitioning can increase quality, but comes at the expense of computing power.