AV1 Codec - Entropy Coding
The entropy coding options in the AV1 codec control how probabilities for different data types (such as coefficients, modes, motion vectors) are adjusted during encoding. Frequent updates (e.g., "Every superblock") make compression more efficient, but also more computationally intensive. The choice of CDF update mode (e.g., "On every frame") also influences how dynamically the probability model adapts.
Advertisement
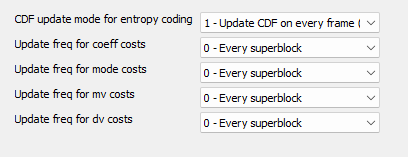
CDF update mode for entropy coding
"CDF update mode for entropy coding" controls how frequently the CDFs are updated. This affects compression efficiency and decodability.
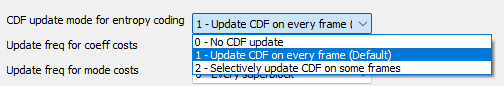
- 0 - No CDF update
CDFs are not updated. This saves computing power but can reduce efficiency
- 1 - Update CDF on every frame (Default)
CDFs are updated every frame. Best compression, but higher CPU load
- 2 - Selectively update CDF on some frames
Only selected frames update the CDFs. A trade-off between efficiency and performance
Update freq for coeff costs
"Update freq for coeff costs" determines how often the probability models for transformation coefficients (e.g., DCT values) are updated. These coefficients represent the fine image details after transformation and are crucial for efficient compression.
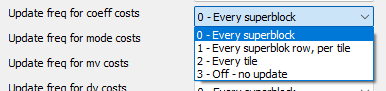
- 0 – Every superblock
Highest accuracy, as it is updated after every 64×64 block (superblock) – best compression, high CPU load
- 1 – Every superblock row, per tile
Lower frequency – once per superblock row within a tile, slightly reduces computational load
- 2 – Every tile
Only once per tile (image area) – faster, but less precise
- 3 – Off - no update
No update – lowest computational load, but potentially worse compression
Update freq for mode costs
"Update freq for mode costs" specifies how often the probabilities for choosing prediction modes are updated. Frequent updates (such as "Every superblock") improve compression by better adapting to image content, while infrequent or no updates save computing power but are less efficient.
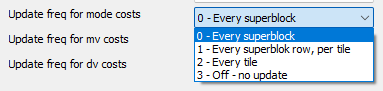
- 0 – Every superblock
Highest accuracy, as it is updated after every 64×64 block (superblock) – best compression, high CPU load
- 1 – Every superblock row, per tile
Lower frequency – once per superblock row within a tile, slightly reduces computational load
- 2 – Every tile
Only once per tile (image area) – faster, but less precise
- 3 – Off - no update
No update – lowest computational load, but potentially worse compression
Update freq for mv costs
"Update freq for mv costs controls how often the probabilities for motion vectors (MV) are updated. These vectors describe how image content moves between frames.
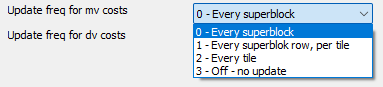
- 0 – Every superblock
Highest accuracy, as it is updated after every 64×64 block (superblock) – best compression, high CPU load
- 1 – Every superblock row, per tile
Lower frequency – once per superblock row within a tile, slightly reduces computational load
- 2 – Every tile
Only once per tile (image area) – faster, but less precise
- 3 – Off - no update
No update – lowest computational load, but potentially worse compression
Update freq for dv costs
"Update freq for dv costs" controls how often probabilities for decoder motion vectors (dv) are updated.
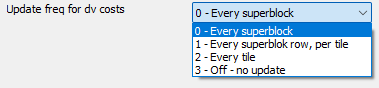
- 0 – Every superblock
Highest accuracy, as it is updated after every 64×64 block (superblock) – best compression, high CPU load
- 1 – Every superblock row, per tile
Lower frequency – once per superblock row within a tile, slightly reduces computational load
- 2 – Every tile
Only once per tile (image area) – faster, but less precise
- 3 – Off - no update
No update – lowest computational load, but potentially worse compression
