AMD AMF H.264 Codec Settings in XMedia Recode: Tips and Techniques
The AMD AMF H.264 (Advanced Media Framework) is a software API (Application Programming Interface) developed by AMD to enable hardware acceleration for video processing, specifically for the H.264 video format.
AMD AMF leverages AMD's GPU hardware to accelerate video encoding and decoding. This reduces the load on the CPU and optimizes performance, which is especially important in real-time video processing.
AMF H.264 also provides features that allow you to control video quality and make adjustments to the bitrate to achieve the best possible balance between quality and performance.
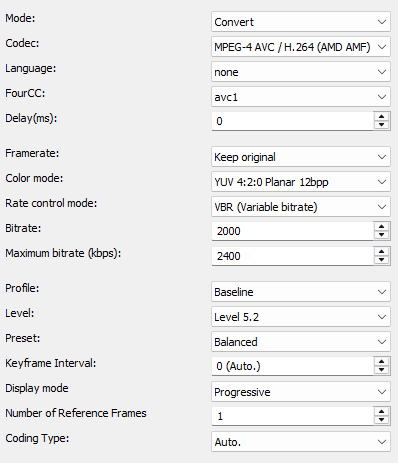
Mode
Determines whether the video is encoded or copied.
- Convert (convert video stream)
- Copy (copy video stream)
Codec
Determines which video codec to use for encoding.
Language
Sets the language that displays when playing the player.
FourCC
Is a 4-byte identifier which specifies the format of a video stream.
Delay(ms)
Sets the delay of the video stream.
Positive values start the stream later.
Negative values start the stream earlier.
Framerate
Sets the frame rate in frames per second.
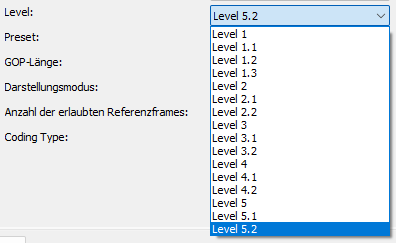
Level
The level setting sets the limit for various parameters such as the maximum resolution, the maximum bitrate and the number of reference frames that can be used in an encode.
Higher levels require more powerful hardware, both for encoding and decoding.
| Level | resolution/frame rate | maximum video bitrate Baseline Extended Main |
maximum video bitrate High |
maximum video bitrate High 10 |
maximum video bitrate High 4:2:2 High 4:4:4 |
| 1 | 128×96 / 30 | 64 kbit/s | 80 kbit/s | 192 kbit/s | 256 kbit/s |
| 1b | 176×144/15 | 128 kbit/s | 160 kbit/s | 384 kbit/s | 512 kbit/s |
| 1.1 | 176×144/30 320×240/10 352×288/7.5 |
192 kbit/s | 240 kbit/s | 576 kbit/s | 768 kbit/s |
| 1.2 | 176×144/60 320×240/20 352×288/15 |
384 kbit/s | 480 kbit/s | 1152 kbit/s | 1536 kbit/s |
| 1.3 | 320×240/40 352×288/30 |
768 kbit/s | 960 kbit/s | 2304 kbit/s | 3072 kbit/s |
| 2 | 320×240/40 352×288/30 |
2 Mbit/s | 2,5 Mbit/s | 6 Mbit/s | 8 Mbit/s |
| 2.1 | 352×288/50 352×576/25 |
4 Mbit/s | 5 Mbit/s | 12 Mbit/s | 16 Mbit/s |
| 2.2 | 352×288/50 720×480/15 |
4 Mbit/s | 5 Mbit/s | 12 Mbit/s | 16 Mbit/s |
| 3 | 720×480/30 720×576/25 |
10 Mbit/s | 12,5 Mbit/s | 30 Mbit/s | 40 Mbit/s |
| 3.1 | 720×576/60 1280×720/30 |
14 Mbit/s | 17,5 Mbit/s | 42 Mbit/s | 56 Mbit/s |
| 3.2 | 1280×720/60 1280×1024/42,2 |
20 Mbit/s | 25 Mbit/s | 60 Mbit/s | 80 Mbit/s |
| 4 | 1280×720/68,3 1280×1024/48 1920×1080/30 |
20 Mbit/s | 25 Mbit/s | 60 Mbit/s | 80 Mbit/s |
| 4.1 | 1280×720/68,3 1280×1024/48 1920×1080/30 |
50 Mbit/s | 62,5 Mbit/s | 150 Mbit/s | 200 Mbit/s |
| 4.2 | 1280×720/145 1920×1080/64 2048×1080/60 |
50 Mbit/s | 62,5 Mbit/s | 150 Mbit/s | 200 Mbit/s |
| 5 | 1920×1080/72,3 2048×1080/67,8 3672×1536/26,7 |
135 Mbit/s | 168,75 Mbit/s | 405 Mbit/s | 540 Mbit/s |
| 5.1 | 2048×1080/112,9 3840×2160/31,7 4096×2160/28,5 |
240 Mbit/s | 300 Mbit/s | 720 Mbit/s | 960 Mbit/s |
| 5.2 | 2048×1080/172 3840×2160/66,8 4096×2160/60 |
240 Mbit/s | 300 Mbit/s | 720 Mbit/s | 960 Mbit/s |
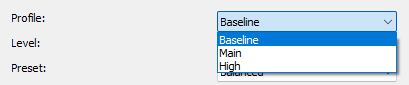
Profile
The H.264 codec profile settings allow you to adjust the compression and quality. There are several profiles, each with different features and capabilities
- Baseline
- Main
- High
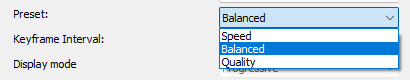
Preset
The preset setting controls the ratio of speed and quality of video encoding
- Speed: Prioritizes encoding speed and ensures that encoding is as fast as possible
- Balanced: Provides a good balance between encoding speed and the quality of the final video
- Quality: Prioritizes image quality, suitable for scenarios where the best video quality is required but at the expense of speed
Keyframe Interval
A GOP is an interval from I-frame to I-frame
Very high GOP lengths result in slightly more efficient compression.
Display mode
Progressive: must be set if the source material is progressive or is converted to progressive by a deinterlace filter.
Interlaced TFF (Top field first): must be set if the source material is Interlaced TFF
Interlaced BFF (Bottom field first): must be set if the source material is Interlaced BFF.
Color mode
Specify output colorspace format.
Number of reference frames
Specifies the number of images that are searched for similarities. Values from 4 to 5 are useful.
A maximum of 16 is possible.
The larger the value, the more time is required for compression.
Coding Type
- Auto.
- CABAC (Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding) is a specific coding method. Instead of variable length bit sequences, it uses a better arithmetic coding that brings between 10 and 20% savings in the data rate.
- CAVLC (Context Adaptive Variable Length Coding) is an efficient coding technique that offers good compression with low computational effort by adapting the code word lengths to the context of the data
CAVLC is less complex than CABAC. CABAC offers better compression, but also requires more computation.
