H.265 Codec: B-Frame Settings
B-frames (bidirectional frames) are video compression frames that use both the previous and next frames to compress data. They offer high compression efficiency because only the differences between the frames are stored.
Advantages:
- Higher compression and smaller file sizes.
- Better video quality at the same bitrate.
Disadvantages:
- More complex decoding, requiring more processing power.
- Increased latency, making them less suitable for real-time applications.
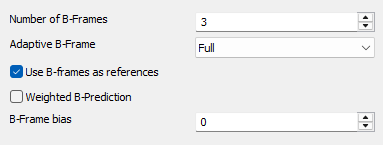
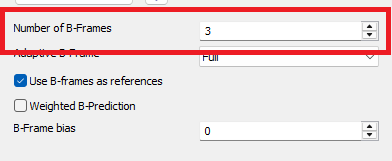
Number of B-Frames
Number of B-frames between I and P
Advertisement
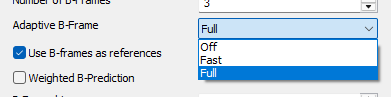
Adaptive B-Frame
Set the level of effort in determining B frame placement.
- Off
the GOP structure is fixed based on the values of --keyint and --bframes.
- Fast
a light lookahead is used to choose B frame placement.
- Full(trellis) default
a viterbi B path selection is performed
Use B-frames as references
B-pyramid function is activated
In the x265 codec (H.265/HEVC), B-Pyramid refers to a technique used in video compression to further increase the efficiency of B-frames (bidirectional frames). This is an extended form of B-frame usage that optimizes the hierarchy of frames and improves compression.
Weighted B-Prediction
Enable weighted prediction in B slices.
Weighted B-Prediction in the x265 codec improves compression and image quality by weighting the influence of neighboring frames on the B-frame prediction. This results in more efficient compression, especially for videos with slower motion or less drastic changes between frames.
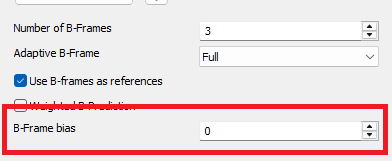
B-Frame bias
Bias towards B frames in slicetype decision.
The higher the bias the more likely x265 is to use B frames.
Can be any value between -90 and 100 and is clipped to that range.